NextGen AgriFood Insights
Empowering sustainable agriculture and food systems through innovation, education, and evidence-based practices
recent posts
- Genomics and Breeding of Six U’s Triangle of Brassica Species
- Thyme Essential Oil in Food Packaging: Phytochemical Insights and Antifungal Mechanisms for Functional Sustainability
- The Efficacy of Chitosan-Based Edible Coatings in Managing Penicillium-Induced Mould Spoilage in Citrus Fruits.
- From Seaweed to Sustainability: Sodium Alginate vs Potassium Alginate for Low Sodium Diets?
- Smart Food Packaging via Electrostatic Coating: A Strategy for Prolonging Fresh Produce Shelf Life
about
Category: Uncategorized
-
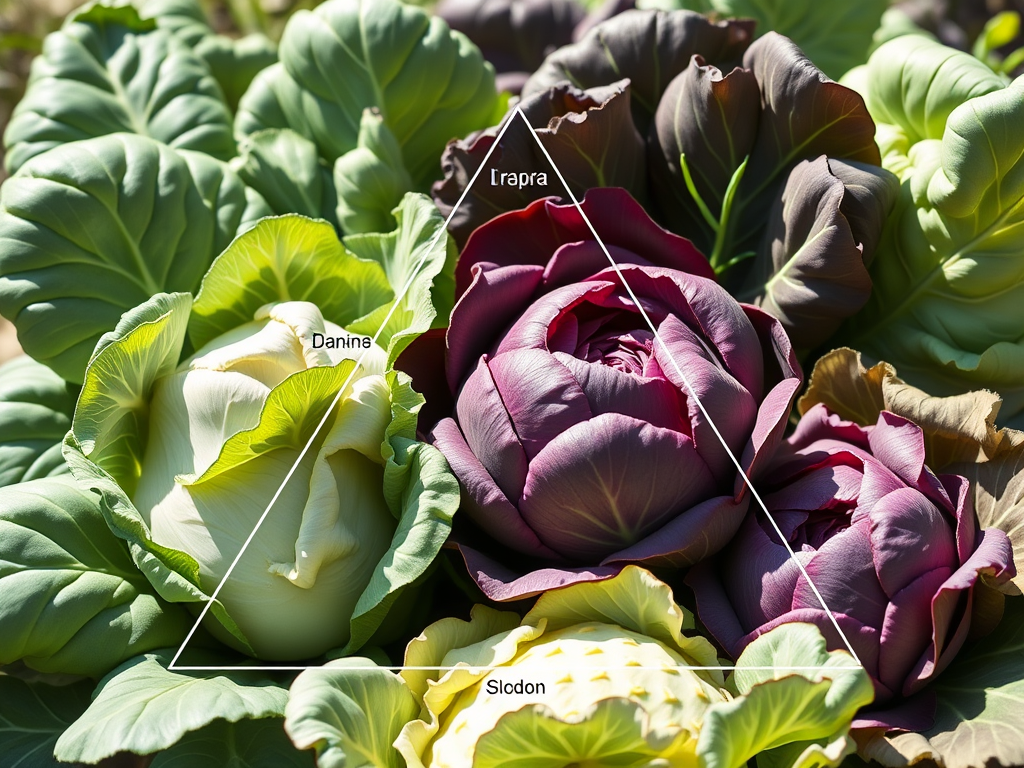

The genetic connections among Brassica species have been identified and verified through experimental crosses between diploid and/or tetraploid Brassica crops, as well as microscopic or karyotyping examination during the synapsis stage of meiosis in these hybrids (Cheng et al. 2014; Zhang et al. 2021a). For instance, F1 plants with a chromosome count of n =…
-
Citrus fruits, including orange (Citrus sinensis), lemon (Citrus limon), grapefruit (Citrus paradisi), and lime (Citrus aurantifolia), and mandarin (Citrus reticulata), are among the most widely cultivated and economically important fruit crops worldwide. Belonging to the Rutaceae family, these fruits primarily grow in tropical and subtropical regions (Topi, 2020). Citrus fruits are valued for their juice,…
-
Introduction Post-harvest losses of fruits are very high, as fruits are highly perishable due to their soft epicarp/exocarp, making them highly susceptible to mechanical damage and post-harvest microbial spoilage, resulting in significant losses. Normally, the shelf life of most fruits is about a week; for some, such as berries, it can be even shorter, just…
-
Post-harvest losses of fruits and vegetables are high due to their perishable nature. Their soft epicarp/exocarp makes them highly susceptible to mechanical damage and microbial spoilage, leading to significant losses. Typically, the shelf life of most fruits is about a week, with some, like berries, lasting only 2–3 days under normal or uncontrolled storage conditions.…
-
Around 300–400 fungal species produce mycotoxins, which are toxic metabolites that contaminate agricultural products and pose significant health risks to livestock, poultry, and humans, even at extremely low concentrations (Latham, 2023). Among them, aflatoxins produced by Aspergillus species (Figure 1) are particularly dangerous, contaminating cereals, oilseeds, spices, and nuts during both cultivation and storage. Aflatoxins,…